rare earth oxides
A review on biomedical applications, prospects, and challenges of rare earth oxides
Authors:
M. Khalid Hossain, M. Ishak Khan, A. El-Denglawey
Highlights:
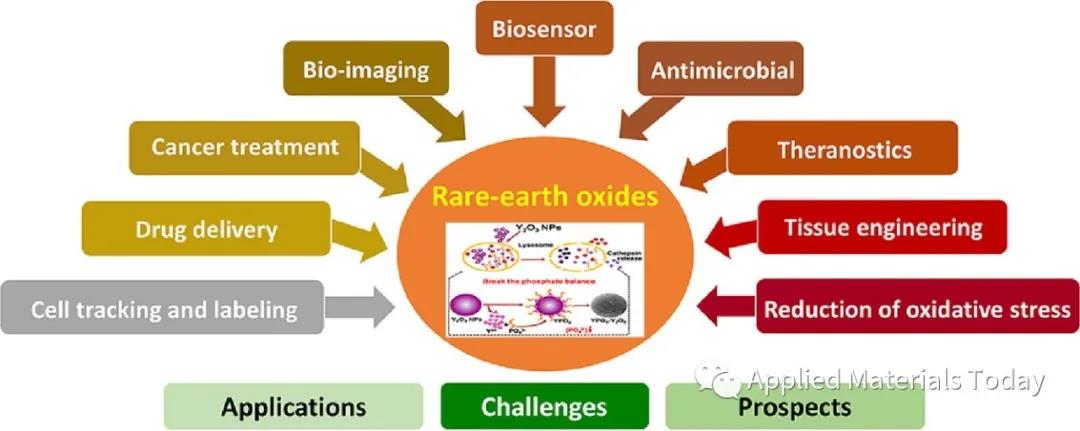
- Applications, prospects, and challenges of 6 REOs are reported
- Versatile and multidisciplinary applications are found in bio-imaging
- REOs will replace existent contrast materials in MRI
- Caution should be exercised in terms of cytotoxicity of REOs in some applications
Abstract:
Rare earth oxides (REOs) have gathered interest in recent years due to their multifarious applications in the biomedical field. A focused review depicting their applicability along with their prospects and associated challenges in this specific field is absent in the literature. This review attempts to specifically report the applications of six (6) REOs in the biomedical field to properly represent the advancement and state-of-the-art of the sector. While the applications can be divided into antimicrobial, tissue engineering, drug delivery, bio-imaging, cancer treatment, cell tracking and labeling, biosensor, reduction of oxidative stress, theranostic, and miscellaneous applications, it is found that the bio-imaging aspect is the most widely applied and holds the most promising ground from a biomedical perspective. Specifically, REOs have shown successful implementation in real water and sewage samples as antimicrobial agents, in bone tissue regeneration as biologically active and healing material, in anti-cancer therapeutic maneuvers by providing substantial binding sites for multifarious functional groups, in dual-modal and multi-modal MRI imaging by providing excellent or increased contrasting capabilities, in biosensing aspects by providing fast and parameter-dependent sensing, and so on. As per their prospects, it is predicted that several REOs will rival and/or replace currently available commercial bio-imaging agents, due to superior doping flexibility, healing mechanism in biological systems, and economic features in terms of bio-imaging and sensing. Furthermore, this study extends the findings with regards to the prospects and desired cautions in their applications, suggesting that while they are promising in multiple aspects, their cytotoxicity in particular cell lines should not be overlooked. This study will essentially invoke multiple studies to investigate and improve the utilization of REOs in the biomedical field.