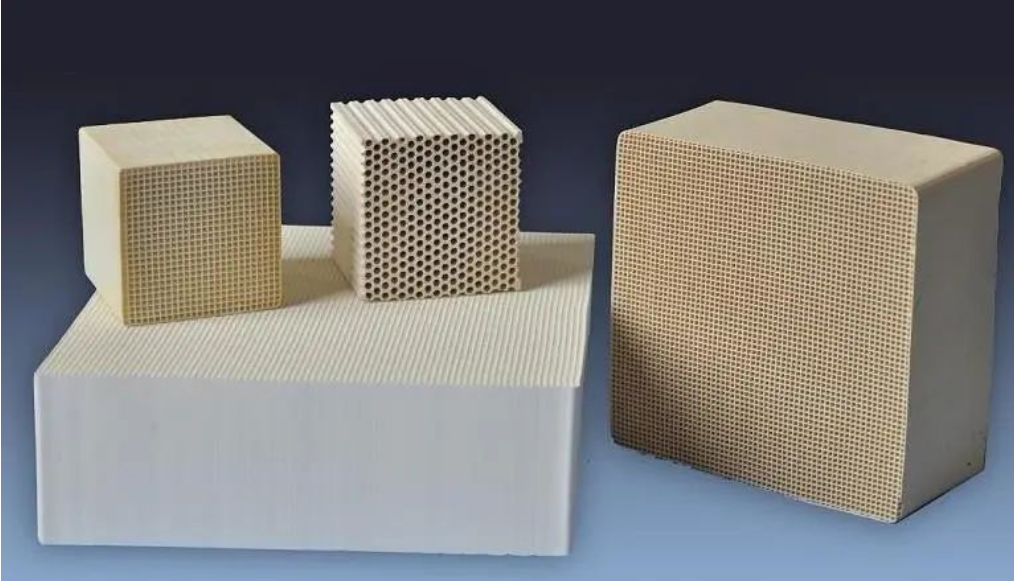
Classification of Rare Earth Purification Catalysts
So far, there are many types of rare earth purification catalysts that have been developed and applied, and their classification methods are also diverse. A simple and intuitive classification is based on the shape of the catalyst, which can be divided into two types: granular and honeycomb. Granular catalysts are typically used γ- Al2O3 is a carrier with a large load capacity, which can load 10% to 20% rare earth and other base metal oxides. It has good impact resistance, but its exhaust resistance is high, which affects its power and economy. Honeycomb shaped catalysts usually use Dongqingshi, mullite, spodumene, and metal alloys as carriers, with a small loading capacity and suitable for loading precious metals. The honeycomb carrier has a small heat capacity, good warm-up performance, power performance, and economic efficiency, and is currently widely used as a carrier. Although the classification method based on the shape of catalysts is simple, the composition of catalysts, especially the active components, cannot be explicitly stated.
If the activity groups of catalysts are different, rare earth catalysts can be divided into two types: rare earth base metal oxide catalysts and rare earth base metal oxide catalysts with trace amounts of precious metal catalysts. The former is a type of catalyst commonly used at present, which has a good purification effect on CO and HC, but slightly poor purification effect on NOx. The latter has a good purification effect on NOx, so it will be the main development direction of tail gas purification catalysts in China.